FAQ
Energy Market
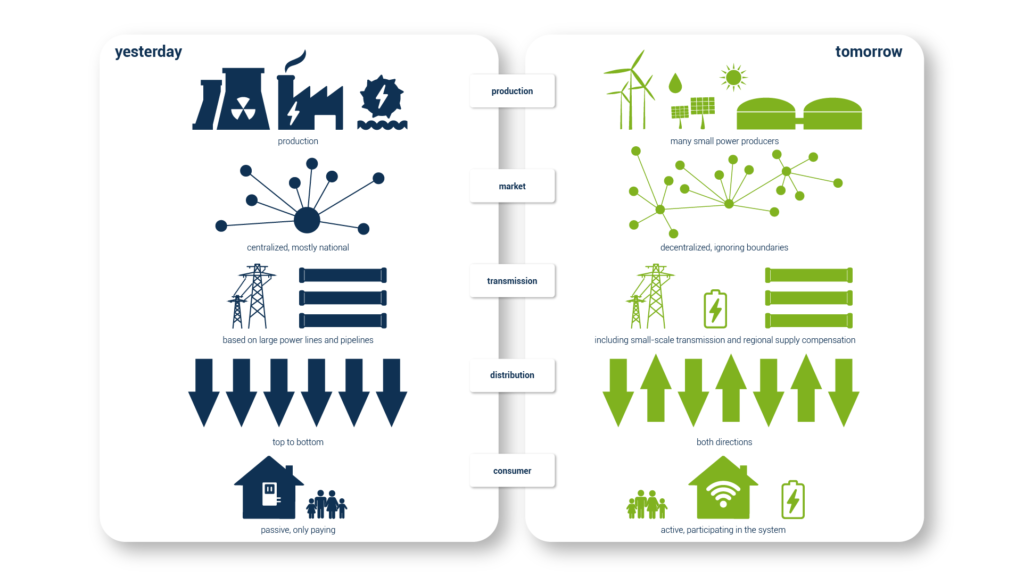
Energy Market yesterday and tomorrow?
The pursuit of net-zero emissions and the REPowerEU Plan, which is the European Union’s strategy for renewable energy, is having a significant influence on the energy market. The plan aims to accelerate the transition to a sustainable, secure, and affordable energy system, and it sets out a number of key targets and initiatives to achieve this goal. This transformation is creating new opportunities for innovation and investment in renewable energy technologies, energy storage, and energy efficiency, while also driving changes in energy consumption patterns and the transportation sector.
The EU Commission predicts that the 28 member countries will produce close to 2 800 TWh of renewable electricity per year by 2030 (compared to 580 TWh in 2020). This creates a huge niche in the market for modern tailor-made solutions that support transformation.
The blockchain-based fully automated community-driven solution is well-positioned to gain traction in the following years of the market transformation.
Why blockchain in the energy market?
Blockchain technology is well-positioned to help in solving some of the key problems of the energy market

Immutability and Traceability
Transparent tracing of the source of energy, which is especially important for the guarantee of origins (GOs). By using a blockchain-based platform, it is possible to create a secure and tamper-proof record of the origin of the energy, to reduce the risk of fraudulent claims of renewable energy certificates.
Decentralization
The energy market is currently centralized, with a few large companies controlling the production and distribution of energy. This leads to inefficiencies, high transaction costs, and a lack of transparency. Enabling the creation of decentralized energy trading platforms that allow individuals and businesses to buy and sell excess energy generated by their renewable energy sources (RES) directly to other consumers without intermediaries.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract between buyer and seller directly written into lines of code. Smart contracts can be used in the energy market to automate and streamline peer2peer energy trading and reduce transaction costs.
Increased transparency
Blockchain technology can help to improve transparency in the energy market by providing a tamper-proof and secure record of energy transactions. This can help to reduce the risk of fraud, improve accountability, and increase trust in the energy market.

Energy Efficiency
Blockchain technology can help to improve energy efficiency by enabling the creation of peer-to-peer energy trading platforms, which can facilitate the use of excess energy generated by renewable energy systems. This can help to reduce waste and promote the use of RES.

Governance (DAO)
The blockchain is well-positioned to establish a community governance model to maintain the reliability and trustlessness of the energy system, especially in the context of energy communities. The community would be responsible for making decisions on the direction of the project, setting rules for participation, and overseeing the verification and issuance of GO certificates.
Why blockchain in the energy market?
What are Energy cooperatives?
Energy cooperatives are a type of energy community that allows members to collectively own and manage energy resources, such as solar panels, wind turbines, or community-scale battery storage systems. Members of energy cooperatives share the costs and benefits of these resources, which can make it more affordable for individuals to invest in renewable energy.
Energy cooperatives can take many forms, such as community-owned solar gardens, cooperative wind farms, or neighborhood-based energy efficiency programs. The goal of energy cooperatives is to provide members with access to clean, affordable, and reliable energy while also promoting local economic development and community empowerment.
In energy cooperatives, members have a say in how the resources are managed and can vote on important decisions, such as how to allocate profits or invest in new projects. This democratic ownership model ensures that the benefits of renewable energy are shared equitably among the community and that decisions are made with the interests of the community in mind.
Energy cooperatives exist in the United States and in Europe and are recognized legal entities in many European countries. The legal structure and requirements for energy cooperatives can vary by country, so it’s important to check with your local cooperative association or national energy agency for specific information about the legal requirements in your area.
In Europe, energy cooperatives have been gaining popularity in recent years as a way to promote community-based ownership of renewable energy resources and decentralize the energy system. Many European countries have policies and incentives in place to support the development of energy cooperatives, such as feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and grants for renewable energy projects.
The European Union has also set ambitious targets for renewable energy production, with a goal of achieving 32% renewable energy by 2030. Energy cooperatives can play an important role in meeting these targets by enabling communities to take ownership of renewable energy projects and promoting local economic development.
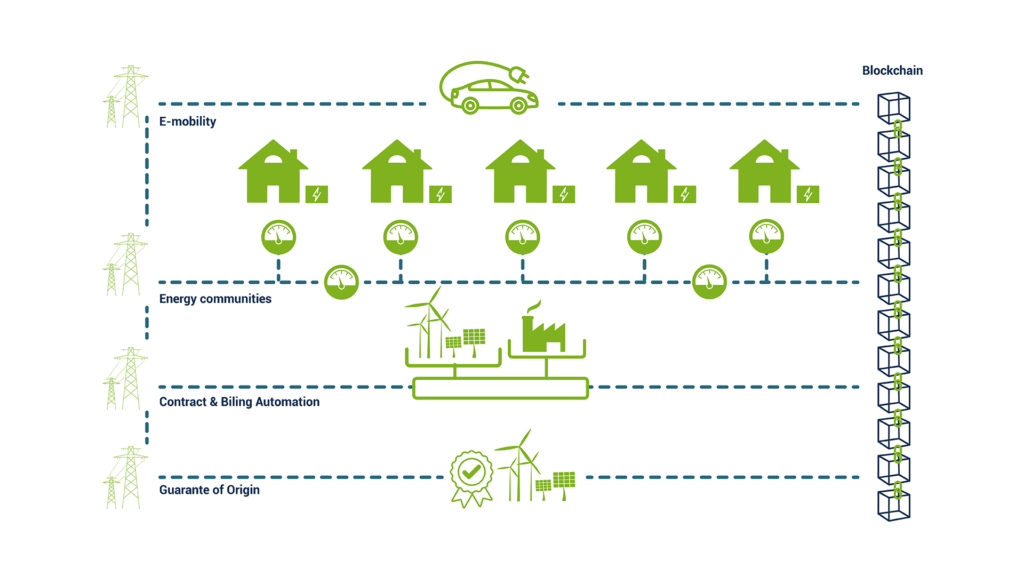
Blockchain network
Leveraging blockchain technology for a community-driven decentralized energy market.
How the blockchain solves the energy market problems?
Blockchain technology has the potential to solve some of the problems faced by the energy market in several ways:
Decentralization: The energy market is currently centralized, with a few large companies controlling the production and distribution of energy. This can lead to inefficiencies, high transaction costs, and a lack of transparency. Blockchain technology can enable the creation of decentralized energy trading platforms that allow individuals and businesses to buy and sell excess energy generated by their renewable energy systems directly to other consumers without intermediaries.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract between buyer and seller directly written into lines of code. Smart contracts can be used in the energy market to automate and streamline energy trading and reduce transaction costs.
Increased transparency: Blockchain technology can help to improve transparency in the energy market by providing a tamper-proof and secure record of energy transactions. This can help to reduce the risk of fraud, improve accountability, and increase trust in the energy market.
Traceability: Blockchain technology can also help to trace the source of energy, which is especially important for renewable energy sources. By using blockchain-based systems, it is possible to create a secure and tamper-proof record of the origin of the energy, which can help to reduce the risk of fraudulent claims of renewable energy certificates.
Energy Efficiency: Blockchain technology can help to improve energy efficiency by enabling the creation of peer-to-peer energy trading platforms, which can facilitate the use of excess energy generated by renewable energy systems. This can help to reduce waste and promote the use of renewable energy sources.
How to realize the vision of an immutable, trustless, and permissionless decentralized energy market?
We believe that the vision of an immutable, trustless, and permissionless decentralized energy market can be achieved through the use of blockchain technology. Blockchain allows for the creation of a secure and transparent ledger of energy transactions that can be accessed and verified by anyone on the network. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and creates a more efficient and cost-effective system for buying and selling energy.
To realize this vision, several key steps need to be taken. First, there needs to be widespread adoption of blockchain technology in the energy industry. This will require collaboration between industry players, regulators, and technology providers to establish common standards and protocols for the use of blockchain in energy markets.
Second, there needs to be a focus on developing decentralized energy generation and storage solutions. This will require investment in renewable energy technologies such as solar and wind, as well as the development of decentralized energy storage solutions such as batteries and smart grids.
Third, there needs to be a regulatory framework that supports the development of decentralized energy markets. This includes policies that encourage the adoption of blockchain technology, promote competition, and ensure consumer protection.
Finally, there needs to be a shift in consumer behavior towards more sustainable and decentralized energy solutions. This can be achieved through education and awareness campaigns, as well as financial incentives such as feed-in tariffs and tax credits for renewable energy generation.
Overall, realizing the vision of an immutable, trustless, and permissionless decentralized energy market will require a collaborative effort between industry players, regulators, and consumers. However, the potential benefits of a decentralized energy market are significant, including lower costs, increased efficiency, and a more sustainable energy system.
What is staking?
Staking is a process by which a cryptocurrency holder locks up some of their coins or tokens to participate in the validation and verification of transactions on a blockchain network. This process helps to secure the network and maintain its integrity.
When a user stakes their coins or tokens, they essentially delegate their voting power to a validator or a group of validators who are responsible for verifying and processing transactions on the network. In return for staking their coins, the user receives rewards in the form of additional cryptocurrency or tokens. These rewards are distributed based on the number of coins or tokens staked, as well as the duration of the staking period.
Staking is a popular alternative to mining, which is the traditional method of validating transactions on a blockchain network. Staking is considered to be more energy-efficient and eco-friendly than mining, as it requires less computational power and electricity. It also allows for greater participation and decentralization on the network, as more users can become validators by staking their coins.
How long does the staking last?
The duration of a staking period can vary depending on the specific blockchain and staking protocol being used. In some cases, staking periods can be as short as a few days or weeks, while in other cases, they may last for several months or even years.
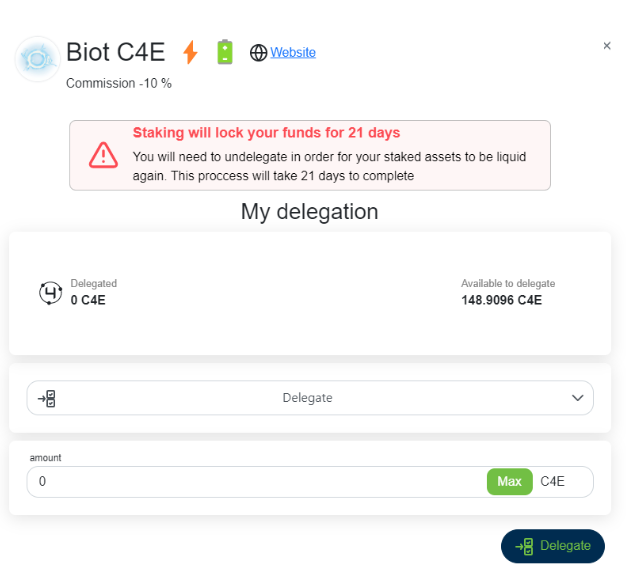
In the case of Chain4Energy, the C4E tokens delegated to the validator can be staked as long as possible but once the user decides to un-delegate they are in the un-bonding state for 21 days.
Is staking risky?
Like any investment, staking involves some degree of risk. The level of risk associated with staking can vary depending on various factors, including the specific token being staked, the duration of the staking period, and the overall market conditions.
One of the main risks associated with staking is the volatility of cryptocurrency prices. If the value of the cryptocurrency being staked decreases significantly, the rewards earned through staking may not be sufficient to offset the losses. In some cases, staking may even result in a net loss of funds.
There is also a risk of potential technical issues or vulnerabilities in the staking process. For example, if a validator or group of validators were to engage in malicious behavior, such as double-spending or censoring transactions, this could negatively impact the stakers who have delegated their voting power to those validators.
However, many users consider staking to be a relatively low-risk investment option compared to other forms of cryptocurrency investment, such as trading or mining. This is because staking generally involves a long-term commitment to a particular cryptocurrency and rewards are earned gradually over time, rather than through speculative trading or short-term investments. Additionally, staking can provide a more predictable and stable source of income for users who are willing to take on the associated risks.
What is the commission?
The commission percent, shown next to each validator, is the percentage of staking rewards that the validator charges as a commission fee. For example, if a validator charges a 10% commission then 90% of the staking rewards will be allocated to you if you delegate to them, while 10% is retained to offset operating costs. Generally, you earn higher rewards from delegating to a low-commission validator. However please note that you should be aware of how reliable the validator is. You could select a validator with 0% commission but offer a bad quality of service and finally, you could be punished as well.
Delegating to a 100% commission validator means you will be allocated none of the staking rewards.
You can check the quality of validators on the independent portal Observatory.zone
How to calculate staking APR?
The Chain4Energy network has programmed inflation of 40M/year of C4E tokens for the first 4 years and the halving of each 4 years.
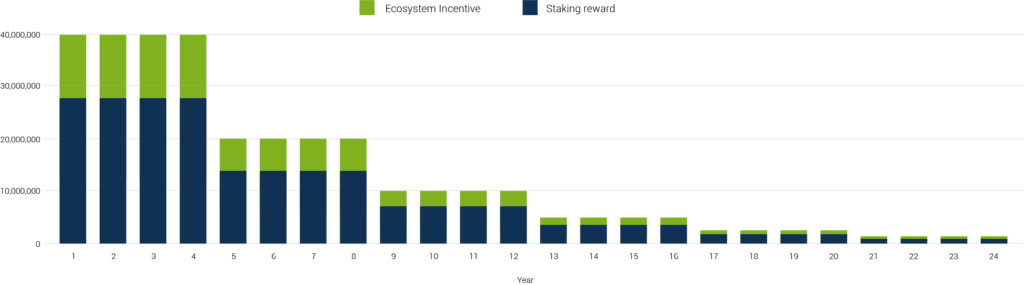
The 70% (28M C4E) of inflation is distributed across all validators and delegators.
Rewards is calculated as such
APR = [Staking Reward]/([Total emission] *[Bonded ration]) * (100% – commission%) * 100
For example for 25% of bonded ration and 5% Validator commission
For Validator:
APR = 28 000 000/(400 000 000 * 25%) * (100% – 0%) * 100
APR = 28%
For Delegator:
APR = 28 000 000/(400 000 000 * 25%) * (100% – 5%) * 100
APR = 26,6%
Please note, the formula will provide an estimate on return because the rewards vary depending on network performance, and the transaction fee and subscription fees. We anticipate and hope to see the rewards increase going forward as the network matures.
The Role of Validators in the Blockchain
In the Chain4Energy blockchain, validators play a critical role in maintaining the security, integrity, and performance of the network. Validators are responsible for verifying transactions, proposing new blocks, and participating in consensus to help ensure that the blockchain remains secure and decentralized.
Validators are selected by token holders through a process called staking. Token holders can delegate their tokens to validators, who in turn use those tokens to secure the network and earn rewards for their services. The more tokens a validator has staked, the greater their chances of being selected to propose a new block.
Validators must meet certain requirements to be eligible to participate in consensus. They must maintain a minimum amount of staked tokens, operate a secure and reliable node, and maintain a certain level of uptime. Validators are also subject to penalties if they fail to follow the network’s rules or engage in malicious behavior.
In addition to participating in consensus, validators also play a role in governance. They can submit proposals, vote on proposals, and participate in on-chain governance decisions to help shape the direction of the network.
How is the validator rewarded?
In the Chain4Energy blockchain, validator rewards are distributed to validators who participate in the consensus process and help secure the network. Validator rewards are paid out in the form of newly minted tokens and transaction fees.
Validators are rewarded for their services based on their share of the total staked tokens on the network. The more tokens a validator has staked, the greater their chances of being selected to propose a new block, and the greater their share of the rewards.
The total reward pool is distributed among validators who successfully validate blocks according to the network’s consensus rules. Validators who fail to follow the rules, or engage in malicious behavior, may be penalized and have their rewards reduced or confiscated.
In addition to validator rewards, there are also incentives for token holders to stake their tokens and participate in the network. Token holders who delegate their tokens to validators can earn a portion of the validator rewards, typically in the form of a percentage of the validator’s earnings.
Blockchain decentralization
Decentralization is a key goal of the Chain4Energy network, as it helps ensure that the network remains secure, resistant to censorship and attacks, and able to operate independently of any centralized control.
To achieve decentralization, the Chain4Energy network uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, which allows token holders to participate in the network’s governance and security by staking their tokens and electing validators to validate transactions and create new blocks.
Validators play a critical role in the decentralization of the network by helping to secure and validate transactions and participating in governance decisions that shape the future direction of the network. Validators are selected based on the number of tokens they have staked and are subject to penalties if they fail to follow the network’s rules or engage in malicious behavior.
In addition to the role of validators, the Chain4Energy network is also designed to be modular, meaning that it consists of multiple independent blockchains (or “zones”) that can operate in parallel and communicate with each other as needed. This helps to reduce the risk of a single point of failure or a single entity controlling the network.
Finally, the Chain4Energy network also has a strong focus on community-driven governance, with token holders able to propose and vote on changes to the network’s rules and parameters. This allows for a decentralized decision-making process that reflects the interests and perspectives of a diverse set of stakeholders.
What is observatory.zone?
Observatory.zone is the service offered by RockawayX Labs.
Builders of Observatory believe as the C4E team that validation is a critical activity in the blockchain ecosystem. Validators have a key influence over the decentralization of the network.
Together we believe decentralization among validators is important to ensure the integrity and availability of the blockchain network and to deter initiatives to adversely affect the network. We identify concentrations of stake across key dimensions and show where they are. Finally, we summarize the decentralization state as a score at the blockchain level and at the validator level.
The Chain4Energy team decided to work closely with RockawayX Labs to focus on the decentralization of the network.
You can check what is the score of chains monitored by the Observatory and also the score of individual validators before making a decision on which you should select.
You can find more on the role of Observatory.zone in the Chain4Energy ecosystem here